Hydrocarbon
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
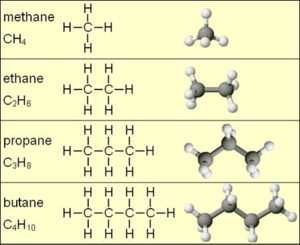
A hydrocarbon is an organic compound consisting entirely of hydrogen and carbon, such as propane, methane, butane, and ethylene.
Most hydrocarbons found on Earth naturally occur in petroleum, where organic matter decomposed anaerobically provides an abundance of carbon and hydrogen which, when bonded, form an endless variety of hydrocarbon chains. Some hydrocarbons, such as ethylene, are produced and emitted by fruit to aid in ripening.
Unburned hydrocarbons and other air pollutants from combustion from automobiles and other engines creates an "oiling" of the soil, making them more resistant to rainfall absorption.[1]
Links
- Hydrocarbon overview - YouTube
References
- ↑ Jacke, Dave, and Eric Toensmeier. Edible Forest Gardens, Volume One. Chelsea Green Publishing, 2005. pp 21.