Taxonomy
Taxonomy is a science of defining and naming groups of organisms based on shared characteristics.
Contents
Levels
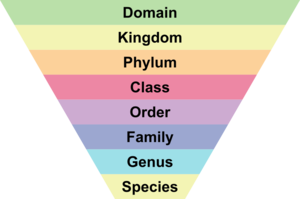
There are multiple taxonomic levels. Broad levels such as a domain have many members with few similarities. Specific levels such as a genus have very few members with many shared similarities.
Domain
A domain is the highest and most broad taxonomic rank. All life form can be classified into a domain. While prone to periodic reclassification, since 1990 there are three domains:
- Archaea - one celled organisms with membranes composed of branched hydrocarbon chains
- Bacteria - one celled organisms that have a substance called peptidoglycan that form their cell wall
- Eukarya - one or multicelled organisms with their genetic material organized in a nucleus
Kingdom
A kingdom is a subdivision of a domain.
Eukarya kingdoms include:
Phylum
A phylum is a major subdivision of an organisim's kingdom.
Some phyla of the animal kingdom are:
- Arthropoda - arthropods
- Chordata - chordates
- Mollusca - mollusks
Some phyla of the plant kingdom are:
- Bryophyta - mosses
- Magnoliophyta - flowering plants
- Pteridophyta - ferns and horsetails
Class
A class is a major subdivision of an organisim's phylum.
Order
An order is a major subdivision of an organisim's class.
Family
A family is a major subdivision of an organisim's order.
Genus
A genus is a major subdivision of an organism's family or subfamily and usually consist of more than one species.
The standards for genus classification are not strictly defined, with different authorities producing different guidelines. However, some general practices are:
- the number of members in a genus is reasonably compact
- that members of a genus share common ancestors
- that members of a genus are distinct
Species
A species is a very specific classification.