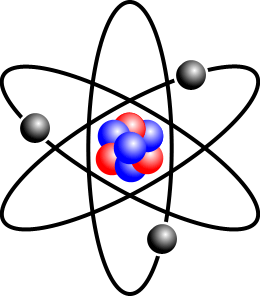
Atom
An atom is the basic unit of matter, comprised of protons and neutrons in its center, and with electrons on the outside. Atoms range from 0.1 to 0.5 nanometers in width[1], with one nanometer about 100,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair[2].
The type of atom, called element, is defined by the number of protons it contains, called its atomic number, such as all carbon atoms having 6 protons and all nitrogen atoms having 7 protons. Standard atoms have an equal number of protons, neutrons, and electrons. If an atom gains or loses electrons the atom is referred to as an ion. If an atom gains or loses neutrons the atom is referred to as an isotope.
Atoms can link with other atoms to form a bond to create a molecule. If a molecule is comprised of different elements it is called a compound, such as two hydrogen atoms bonding with one oxygen atom to create water, or two hydrogen atoms bonding with two oxygen atoms to create hydrogen peroxide.